What is SAN (Storage Area Network)?
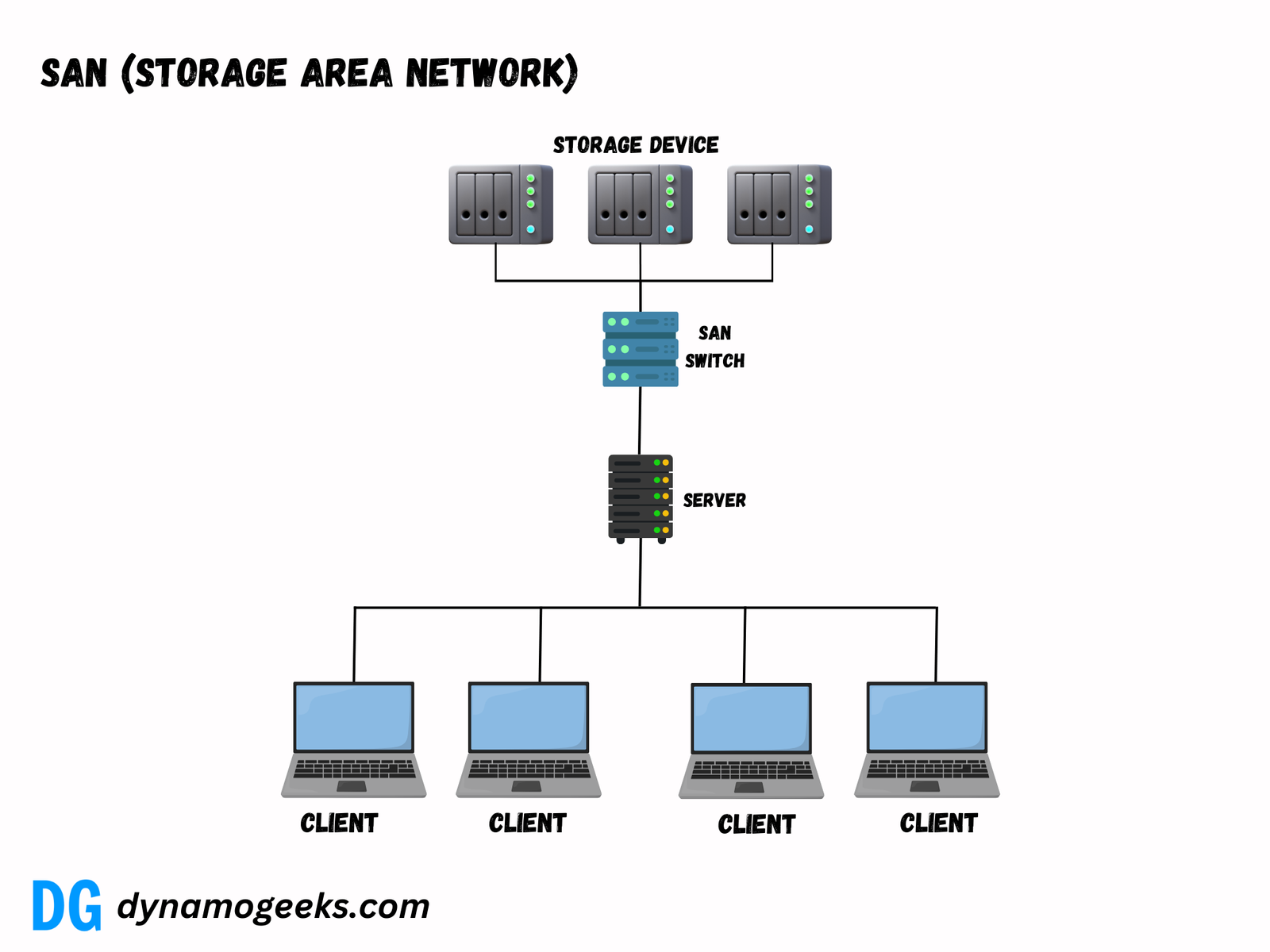
Storage Area Networks (SANs) are high-performance networks specifically designed to provide fast and reliable access to centralized, block-level data storage. These networks connect servers to storage devices in a way that enhances data availability, speeds up processing, and supports seamless data sharing within a system. SANs play a crucial role in enabling businesses to manage their data efficiently and meet the increasing demands for storage and retrieval.
1. Why Use SAN?
In a world where data is the backbone of businesses, having efficient and scalable storage is critical.
SANs help organizations handle large amounts of data efficiently. They reduce bottlenecks and ensure faster access to vital information.
Unlike traditional storage methods, SANs separate storage from servers, making them more versatile and reliable.
2. Where to Use SAN?
SANs are commonly deployed in environments that require high data availability and large-scale storage. These include data centers, cloud infrastructures, and enterprise-level IT systems.
SANs are especially vital in industries like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, where data must be processed quickly and stored securely.
3. Who Should Use SAN?
Organizations that deal with massive volumes of data should consider using SAN. Businesses with high-performance computing needs or those requiring robust disaster recovery plans can benefit significantly from SAN.
It’s an excellent solution for enterprises and mid-sized companies with complex data storage requirements.
4. Advantages of SAN
- High speed: SAN ensures high-speed access to data by connecting storage devices and servers using a dedicated network.
- Scalability: It’s easy to add more storage as your needs grow.
- Enhanced security: SAN provides features like snapshots, replication, and backup support to protect data.
- Centralized management: IT teams can manage storage systems more efficiently from a single interface.
- Reliability: SAN reduces data loss risks by incorporating redundancy and failover mechanisms.
5. Disadvantages of SAN
- High cost: The initial setup requires significant investment in specialized hardware and software.
- Complex maintenance: SANs require skilled IT professionals for operation and troubleshooting.
- Intricate architecture: Managing a SAN involves handling complex configurations, making it prone to errors if not managed properly.
6. Limitations of SAN
Despite their benefits, SANs are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Small businesses with limited data storage needs may find SANs unnecessary and overly expensive.
Their dependency on specialized infrastructure means they can be prone to downtime if a critical component fails.
Additionally, latency issues can arise if the SAN is not properly configured or maintained.
7. Alternative Options to SAN
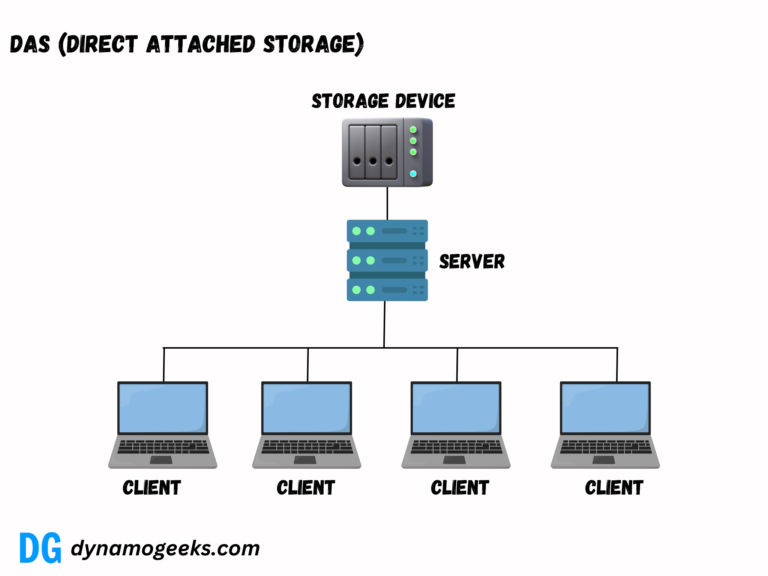
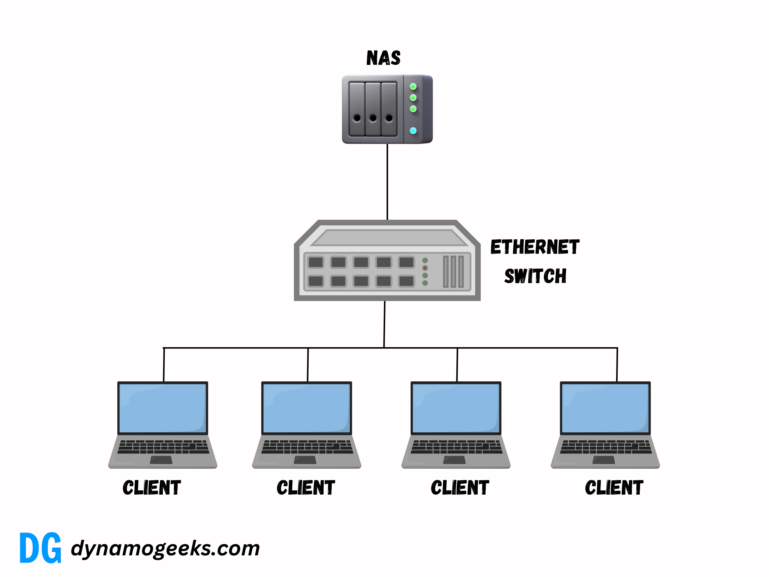
For organizations that don’t need a SAN’s complexity, alternatives like Network Attached Storage (NAS) or Direct Attached Storage (DAS) might be better.
NAS is ideal for file-level storage, and DAS is suited for small-scale deployments. Cloud storage services can also replace SANs for businesses looking for cost-effective, scalable, and remote storage solutions.
8. Who Shouldn’t Use SAN?
Small businesses or startups with minimal data storage requirements might not benefit from SANs.
The high cost and complexity of implementation make SANs unsuitable for companies with tight budgets or those without in-house IT expertise.
Similarly, organizations with low-performance storage needs may find simpler and cheaper solutions more appropriate.
9. FAQs About SAN
1. What is the main purpose of a SAN?
The primary purpose of a SAN is to provide high-speed, block-level storage access to servers.
2. How is SAN different from NAS?
SAN operates at the block level, while NAS works at the file level.
3. Can SAN be used in a cloud environment?
Yes, SANs are often used in hybrid and private cloud environments for robust storage solutions.
4. Is SAN secure?
Yes, SANs offer advanced security features, but proper configuration and management are essential.
5. What is Fibre Channel in SAN?
Fibre Channel is a high-speed networking technology used to connect SAN components.
6. Can small businesses benefit from SAN?
Typically, small businesses find SANs cost-prohibitive unless they have specific high-performance requirements.
7. What hardware is required for SAN?
SANs need storage arrays, switches, and host bus adapters, among other components.
8. How does SAN improve disaster recovery?
SANs support replication and backup, ensuring data availability during disasters.
9. Are SANs scalable?
Yes, SANs are highly scalable, making it easy to add storage as business needs grow.
10. What protocols do SANs use?
Common SAN protocols include Fibre Channel, iSCSI, and FCoE (Fibre Channel over Ethernet).
10. Conclusion
SANs are powerful storage solutions designed for organizations with demanding data storage needs. They ensure fast, secure, and scalable access to data, making them ideal for enterprise-level applications. However, they may not suit every organization due to their high cost and complexity. Evaluating your business needs carefully will help you decide if SAN is the right choice for your organization.
Summary
Storage Area Networks (SANs) provide high-speed, block-level storage for enterprise environments. They are suitable for industries requiring robust data management and scalability. While SANs offer numerous benefits, such as speed and reliability, they also have drawbacks, like high costs and complexity. Organizations must weigh the pros and cons to determine if SAN aligns with their requirements.